Part 2 of 2 – Trees for root spaces greater than 10 feet wide
When an ash tree is the friendly cover above your patio or picnic table, and it is doomed to fall to the plague of emerald ash borer, its loss is a personal one. Here’s some consolation: in that location, with park-like room for roots to spread, many species can be expected to grow well and quickly.
Choose from this list and score one for diversity. By planting one of these excellent but underused species, you’ll help diminish the chance of whole-neighborhood defoliation during some future insect or disease attack.
Trees for root spaces at least 10 feet wide
These trees need larger boulevards and islands, where roots have at least 10 feet to spread in all directions:
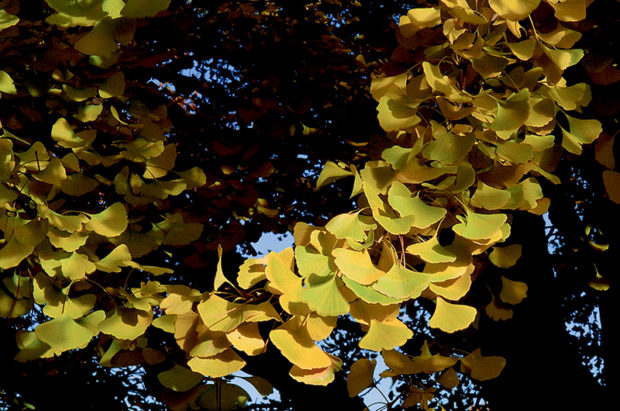
Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba, fruitless male varieties such as ‘Autumn Gold’ and ‘Santa Cruz’) 50 to 80’ tall with a variable spread (‘Santa Cruz’ is very wide, ‘Autumn Gold’ just a bit more than half as wide as tall). Grows 12” or more per year in its youth, slower as it matures. Flowers are inconspicuous. Fall color can be a superb gold. Female trees are not desirable as the fallen fruit is malodorous. Full sun. Prefers deep, moist, sandy soil but will tolerate almost any situation.
Hackberry (Celtis occidentalis) 40 to 60’ tall and wide, may be larger. Grows 1 to 2’ per year. Grows in almost any soil and moisture condition, in full sun. Makes no show of flower or fall color. Hard-seeded, berry-like fruit loved by birds and small mammals. This is another of many native trees that are just being discovered for use in the landscape. Like the ash, it’s a tree that rarely stars, yet always fills a supporting role. Some selections have been made, such as ‘Prairie Pride’ with especially lustrous leaves and a broad crown or ‘Windy City’ for a fast growth rate and especially wide spread reminiscent of its relative, the American elm.
Hardy rubber tree (Eucommia ulmoides) 40 to 60’ tall and wide. Grows 12 to 18” per year. Lustrous dark green foliage that’s pest free (and so it’s wonderful to sit under!). Inconspicuous bloom. No fall color. Full sun and almost any type and condition of soil. This tree fits the bill for people who want a non-fussy, relatively fast-growing, pest-free shade tree that does not drop fruit or seeds.
Turkish filbert (Corylus colurna) 40 to 50’ tall and about half as wide. Grows 12-18” per year. Nothing worth seeing in its tiny flowers or fall color. Nuts ripen in fall. Dark green foliage is pest free. In full sun and well-drained soil can tolerate almost any other adverse condition, including the droughty soils that cause scorch on maples.

Yellowwood (Cladrastis kentukea) 30 to 50’ tall. Wider than tall. Grows about 12” per year. Fragrant white flowers in large pendant clusters in June. Smooth gray bark. Full sun and well-drained soil.
Trees that should not have any restriction to their roots
These are trees that belong in back yards, parks and wide open spaces.

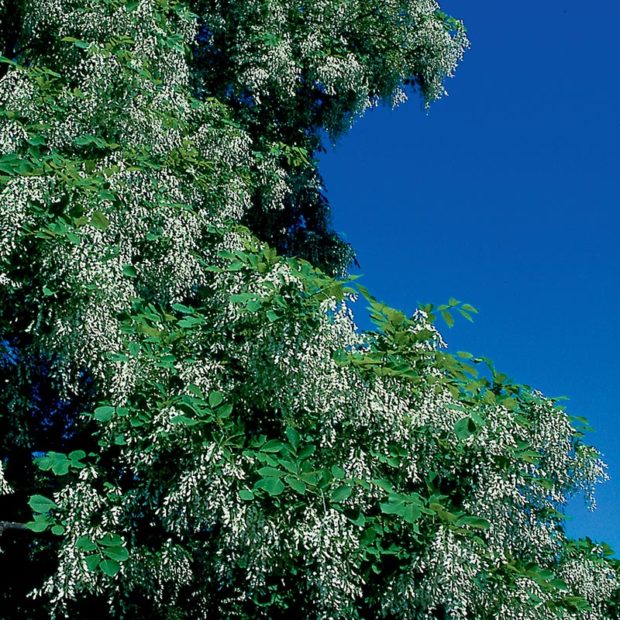
American linden (Tilia americana) 60 to 80’ tall and 2/3 as wide. Grows 12 to 18” per year. Small white flowers in June are fragrant enough to carry across a yard and very attractive to bees—thus this is called “bee tree.” Fall color sometimes yellow. Full sun to half sun. Almost any soil.

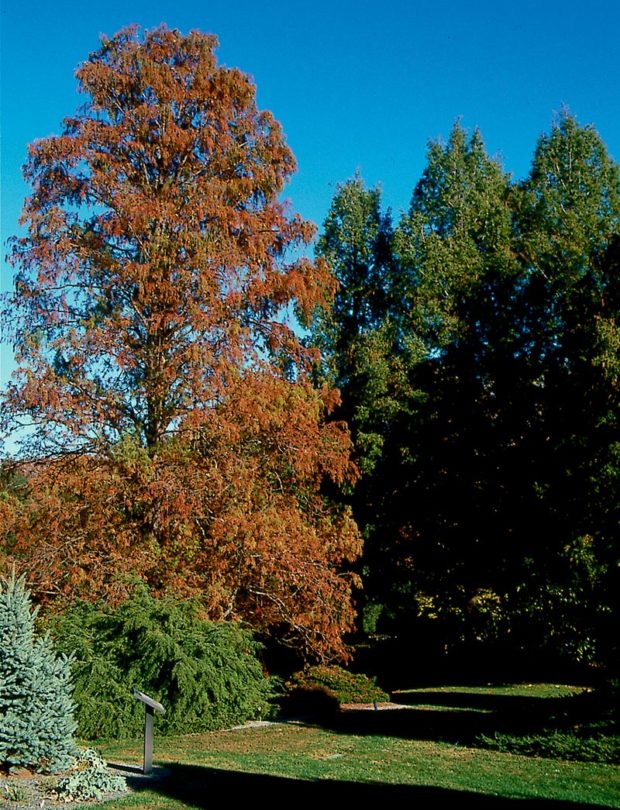
Bald cypress (Taxodium distichum) 50 to 70’ tall and half as wide. Pyramidal. Grows 1 to 2’ per year. Fern-like foliage emerges yellow green and fades to yellow or orange-brown before dropping in fall. Shaggy red-brown bark and buttressed trunk base are attractive. Full sun. Moist to wet soil.
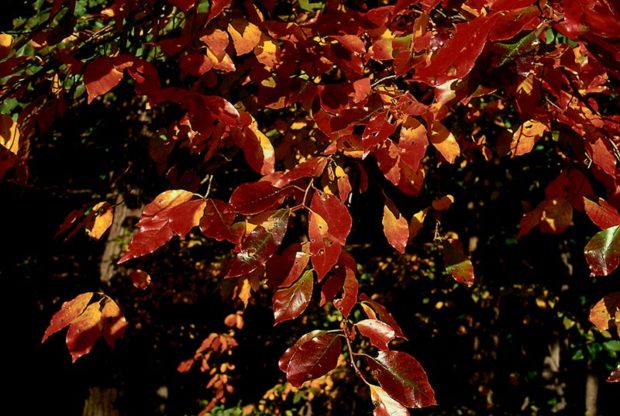

Black gum (Nyssa sylvatica) 30 to 50’ tall and 2/3 as wide. Grows 12” per year. Its bloom is inconspicuous but fall color is stupendous, from yellow orange to deepest scarlet. Small fruits ripen in early fall and are eaten by birds. Full sun or part shade. Deep, moist, well-drained soil. Don’t site it in harsh winds.
Bur oak (Quercus macrocarpa) 70 to 80’ tall and wide. Can be larger. 8 to 12” growth per year. Nothing to note in terms of flower or fall color. Full sun. Most any soil. More tolerant of city conditions than almost any other oak.
Dawn redwood (Metasequoia glyptostroboides) 70 to 100’ tall, 25’ wide. The tree is an impressive pyramidal form. Grows 3’ a year. Inconspicuous flower. Foliage is ferny, very attractive and sometimes red-orange in fall. Bark is shaggy red-brown, easy to like. Full sun. Prefers moist, well-drained soil but is very tolerant of wet soil. Pest problems are very rare.

Kentucky coffeetree (Gymnocladus dioicus) 60 to 75’ tall, not as wide as tall. Can be larger. Grows about 12” per year. Flower is insignificant. Female trees can bear large, hard pods; if this is unacceptable, hold out for the male variety ‘Prairie Titan’ or ‘Stately Manor.’ Fall color may be a good yellow. It can aggravate fastidious rakers since in the fall the leaves, the ribs that connect the leaflets, and the seed pods drop at different times. Full sun. Deep, moist soils are best, but the tree will tolerate almost any city condition. This tree got its name when early American settlers used the seeds as a coffee substitute, but we are now told its seeds are toxic.
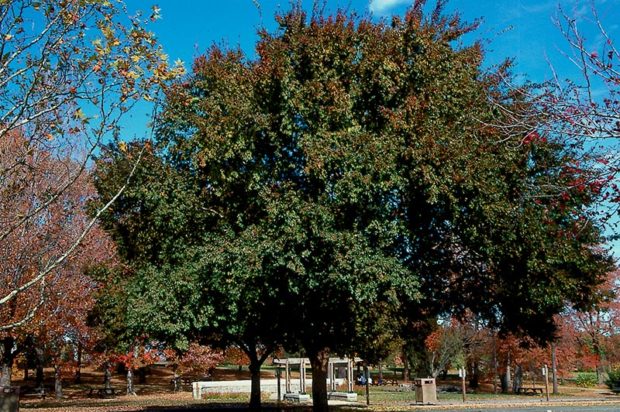

Lacebark elm (Ulmus parvifolia) 40 to 50’ tall and wide. Grows 1 to 2’ per year. Inconspicuous flower. Fall color may be yellow or red-purple. Mottled, peeling bark is a plus in winter. Full sun. Moist, well-drained soil is best but it tolerates many soil conditions.
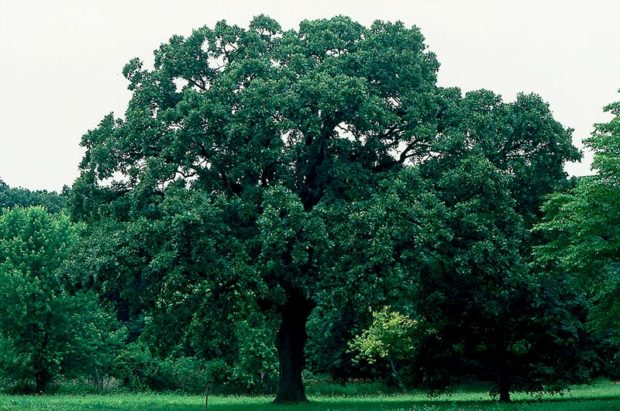

Sawtooth oak (Quercus acutissima) 40 to 60’ tall and wide. Grows 2’ per year during its first twenty years. Golden catkin flowers in spring can be attractive. Foliage is very clean, deep green in summer, often a good yellow in fall. Acorns drop early in fall. An impressive, high-branched shade tree. Full sun. Well-drained soil.

Shingle oak (Quercus imbricaria) 50 to 60’ tall and wide. Can be larger. Grows 12 to 18” per year. Leaves unfurl red, are lustrous dark green in summer and become yellow to red-brown in fall. Full sun. Moist, well-drained soil.
Swamp white oak (Quercus bicolor) 50 to 60’ tall and wide. Can be larger. Grows about 12″ per year. With age, develops an impressive, stout trunk and deeply furrowed bark. Fall color can range from yellow to maroon. Full sun. Moist to wet soil.
Read More: Part 1 – Trees for root spaces less than 10 feet wide
Article by Janet Macunovich and photos by Steven Nikkila, www.gardenatoz.com.